O-Medical education
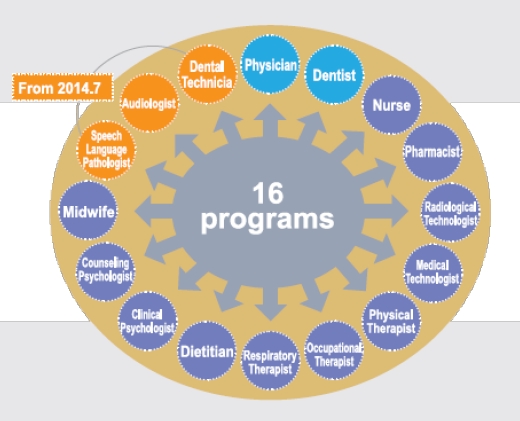
In response to the rapid changes in medical knowledge and environment and the expectations of the general public towards healthcare professionals, cultivation of core competence has recently become an important key for the development of medical education. The World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) proposed the concept of continuous unity in medical education by using institutional medical education as a starting point to integrate education and training, and life-long professional capabilities through continuous professional development. Based on previously mentioned concepts, the Ministry of Health and Welfare has contracted this Committee to plan for a post-graduate clinical training system for medical staff to connect the clinical education between school education and post-graduation. This allows new medical staff to receive standardized professional training base on the existing school education and the guidance of experienced clinical instructors, to cultivate professional core competencies in order to achieve independent practical nursing capabilities, and ensure the quality of healthcare services. Since 2007, the Ministry of Health and Welfare has supported and reimbursed each teaching hospital in executing training for post-graduate medical staff through “Instruction Fee Reimbursement Programs for Teaching Hospitals.” This Committee has invited 11 medical professional groups and specialist to establish a post-graduate clinical training system, and to set up the training items for each medical field, training targets, training times, training methods, evaluation standards (methods), and training locations and conditions, and has included the training in the scope for hospital accreditation as a basic requirement of execution for each institution. In 2014, the three occupational classes, audiologist, language therapist and dental technician, were included into the entire program.
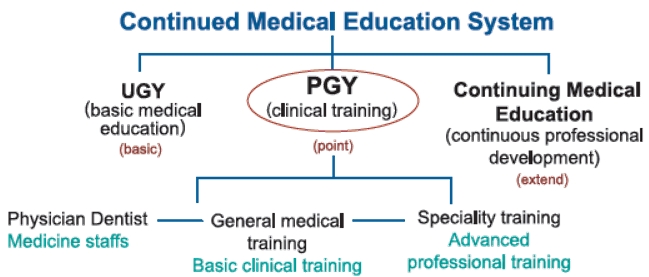
Post Graduate Year, PGY
Physicians
Over the years, medical students in Taiwan received organ-focused, disease-oriented and specialty treatment training at different specialty departments after graduating from medical schools, in order to develop their specialties and sub-specialties. However, the problems and deficiencies of such a system was exposed during the SARS outbreak in 2003. Therefore, the Department of Health proposed the Clinical Education Training and Reform Program after the epidemic was stabilized. In July 2003, the Department of Health officially announced the Post Graduate Year Program to rectify the resident physician training system’s overemphasis on early specialty training.
In consideration of the training capacity, faculty size and training venue readiness, the JCT implemented the program in three stages. The first stage took place between July 2003 and June 2006. During this period, resident physicians were required to receive general medicine practice for three months in the first year of their residency. With the support and concerted efforts of hospitals and society, the overall teaching atmosphere of teaching hospitals in Taiwan has been improved, and the spirit and concepts of general medicine were thus established. The second stage began in July 2006. At this stage, the 6-month general medicine training was designed to lend into curriculum guidelines of specialty training for postgraduate physicians, and the model for postgraduate general medicine training was established. The third stage started from July 2011. The postgraduate participated the joint training group that “focuses on the main training hospital” to receive training by the selection system. Now, PGY training has entered a new milestone, because they are no longer the first year resident physician of each sub-specialty, but a PGY physician.
Since the 2013 academic year, the Ministry of Education has amended the year of study for medical school from 7 years to 6 years. In combination with the PGY training for the period of 2 years after graduation in the future, the overall medical education has more comprehensive planning and connection from integrated medical education to school and to clinical. The JCT implemented this program on commission of the Ministry of Health and Welfare in organizing a pilot PGY training system (divided into internal medicine, surgery, gynecology, and pediatric trainings in general medicine) starting with three medical centers in the 2013 academic year to connect specialty training in the future. We hope that the graduate students from the 6-year education system have a more rigid continuous unity in medical education all the way from school education, post-graduate general medical training to specialty training.
Dentist
Base on the achievements of physician postgraduate training program, the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) started to expand scope of trainees to other medical professionals in 2007, and the dentists were included in 2010.
MOHW announced dentists shall complete two-year postgraduate general medicine training before participating in the specialist training. Moreover, who want to be the supervising physician of clinics shall be limited to those who have received at least two years of medical training at hospitals or clinics designated by the central competent authority.
Therefore, MOHW launched “Two-Year of Dental Post Graduate Year Program”. This program includes 50 hours fundamental training, holistic dentistry (compulsory courses) for 18 months, and elective courses for 6 months. Compulsory courses also include community dental training, oral and maxillofacial surgery clinic, and emergency treatment.
MOHW also provided teaching subsidization for the certified training institutions. Up to now, there were 509 institutions (91 hospitals and 418 dental clinics) certified by MOHW, approximately 65% of dentists received training in hospitals and 35% in dental clinics.

